I attended the preview of the SGX CSP Module 3 Fundamental Analysis course on 24 July 2018. The course is to be conducted by Chua I-Min on 3 evenings on 17 August, 24 August and 31 August from 7 pm to 10 pm.
Why choose fundamental analysis?
As an introduction, I-Min explained how someone who practises fundamental analysis (FA) thinks. When he buys a stock, he thinks of it as a business venture and himself as the owner of the business. He explained the difference with another method, which is using technical analysis, whereby investors buy or sell using charts. Technical analysis (TA) believes that charts map out human behaviour.
I-Min advises that for newbie investors, they should use the first 6 months to figure out if TA or FA suits them. You should either be a TA or a FA.
When people asked I-Min why he chooses to be a FA and jot TA, I-Min explains that a lot depends on personality. When I-Min buys into stocks, he is prepared to hold for 3 to 5 years. If you want to be a FA, you need to be patient. If you are impatient and can’t wait long, maybe TA is better. He shared that he has a friend who is TA, and his friend advised that to be a TA, one needs to be heartless. For example, if he bought a stock at $1.00 and it dropped to $0.80, he would not think too much and would cut loss.
Why not use technical analysis and fundamental analysis together?
I-Min said that if FA is good and TA is good, people asked why not do both, so that FATA (发达meaning prosperous). I-Min explained that for a newbie, he would not encourage to do both FA + TA at the same time. This is because sometimes FA said ‘buy’ but TA would say ‘sell’. For example, now STI is 32XX, beginning of 2018 is 34XX, so TA say prepare to short, but for FA, it could be prepare to buy as a lot of stocks are cheap. I-Min said he uses TA sometimes, but he is mainly using FA.
Design of SGX CSP Module 3 Fundamental Analysis
I-Min explained the course structure briefly.
Professional course targeted at:
- clients serving professionals
- investors keen to perform more comprehensive analysis. (However, professional doesn’t mean more difficult!)
Facilitation based learning
- Focus more on subjective content for discussion
- Some hard facts / calculation may be covered briefly
- Participants are expected to contribute and self-learn
Assessment
- Discussion
- MCQ
Fundamental Analysis
For I-Min, the order of analysis will start with the most important (from left to right):
business/industry analysis -> financial statement analysis -> pricing analysis -> risk analysis
To I-Min, the most important part of FA is the business model analysis, not what a lot of people thought FA is about—focusing on financial statements, P/E ratio etc. We can use the SWOT analysis to help us analyse the business of the company.
I-Min gave the case study of Capitaland using the SWOT analysis.
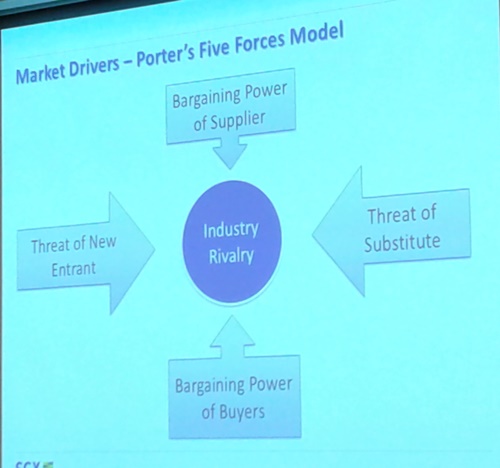
We can look at the Market Drivers – Porter’s Five Forces Model.
I-Min used the example of the company ComfortDelGro, which is a taxi rental transportation company.
When Uber and Grab came in, they disrupted the company. But can it kill ComfortDelGro? No, because ComfortDelGro still can rent out cars.
However, if driverless cars come in, it might kill ComfortDelGro because driverless cars optimise the number of people to carry. Also, it can save parking spaces.
Investment theme of the year
We need to look at investment theme of the year. For example, I-Min shared how in one year the theme was education and he bought into an educational company and there were stock splits and the price of each share went up multi-fold. In another year, the theme was construction and he bought into all the different construction companies and the stock all went up by 50%.
What are the investment themes for this year? I-Min shared a few here.
- Real Estate
- Healthcare
- Technology
Other topics covered in SGX CSP Module 3 Fundamental Analysis course
Management and Corporate Governance: What are their qualifications and experience?
How to seek out red flags? Use of financial ratios e.g. Net Profit Margin, Current Ratio, Debt to Equity ratio, Interest coverage ratio etc.
- Other red flags and business warnings e.g. off-balance sheet transactions like operating leases versus purchases
- Distribution of earnings: dividends, bonus share
- Other actions: mergers and acquisition, delisting
- Pricing analysis: different industries make use of different indicators (P/E, P/B, and dividend). For example, for property, P/B is preferred whereas for REITS, we look at dividend yield rather than P/E
Economic analysis
I-Min advised that to do fundamental analysis, we need to have opinions. How to get opinions? We can look at macro indicators such as unemployment rate, study events, e.g. currently there is the trade war. Do you think it will end soon, or it will get worst?
Historically, STI is trading between 8x to 16x and today, P/E of STI is round 10x. For US Dow Jones Industrial Average, historical range is 10x to 20x and it is now at 18x. Now, US market is expensive and Singapore market is cheap. So how do we proceed?
How was the first lesson of the course on 17 August 2018?
A lot of materials were covered on 17 August 2018 during the first lesson. I will write about the first lesson of the course in another post shortly. Stay tuned.